As seen in the published EEA Bathing Water Quality in 2020, the number of bathing waters in Europe is increasing every year. In 2020, countries identified 22 276 bathing sites, 19 less than the previous year and 716 more than in 2015. Two thirds of bathing sites are located along the seacoasts of Europe.
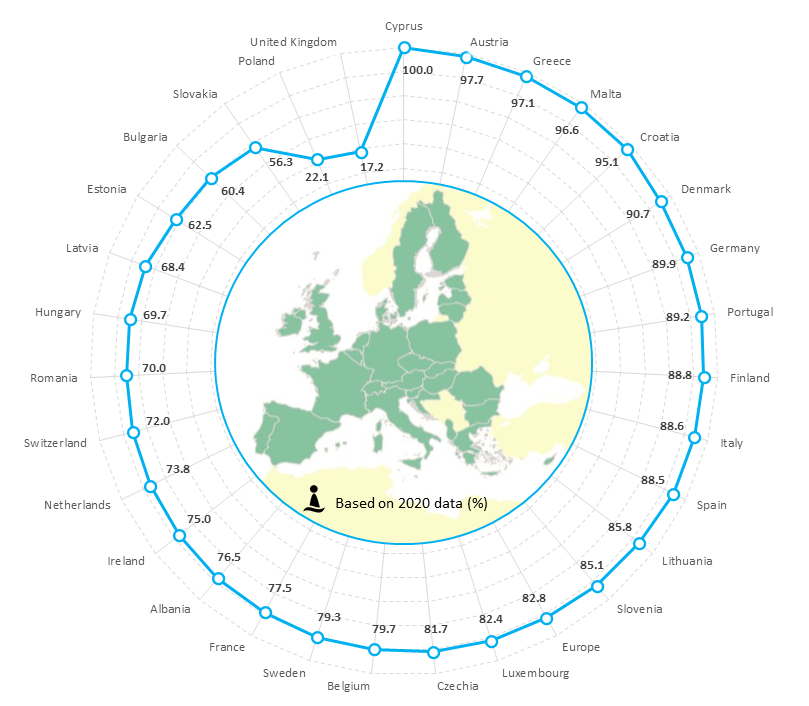
Bathing water quality in the EU remains high. Since the adoption of the Bathing Water Directive in 2006, the share of excellent sites has been growing continuously; in 2020, it represented 83 % of bathing sites in the EU. The minimum water quality standards were met at 93 % of sites.
The quality of coastal sites is generally better than that of inland sites. In 2020, 85.4 %, of the EU coastal bathing sites were classified as being of excellent quality compared to 77.5 % of inland sites.
The share of poor-quality sites has dropped since 2013. In 2020, poor bathing waters constituted 1.3 % of all sites in the EU, compared to 2 % in 2013. This shows improvements in the management of poor bathing sites in Europe.
The quality of a number of bathing waters could not be classified due to an inadequate number of samples in relation to the restrictions caused by the epidemic. For the season of 2020, 1 309 (6.0 %) EU bathing waters are not classified, compared to 806 (3.7 %) in 2019.